Luxury Boom in Nigeria: Million-Dollar Homes Transform Skylines and Ignite Concerns
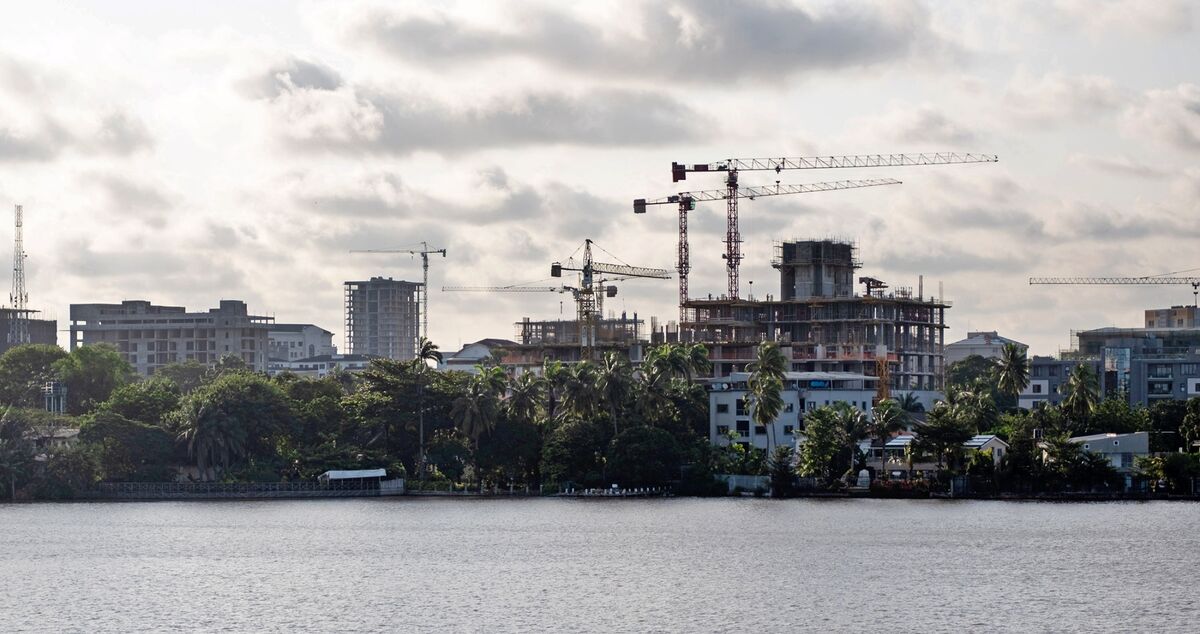

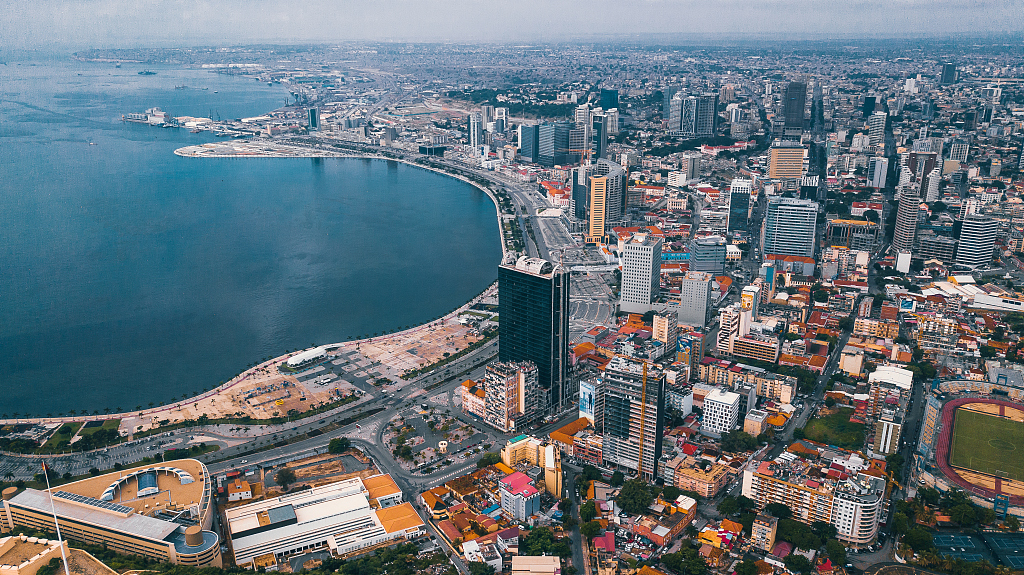
Nigeria’s real estate landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Once characterized by modest residential developments and informal housing clusters, the country’s major cities are now punctuated by soaring luxury apartments, lavish villas, and million-dollar homes. From Lagos to Abuja, these high-end properties are reshaping urban skylines and signaling a growing appetite among wealthy investors and expatriates—but not without raising red flags for urban planners, policymakers, and local communities.
The Rise of Million-Dollar Residences
In Lagos, Nigeria’s economic hub, the skyline has changed noticeably over the past decade. High-rise luxury apartments now dominate Victoria Island and Lekki, while sprawling villas redefine the landscape in Banana Island. In Abuja, the capital city, upscale gated communities like Asokoro and Maitama have become synonymous with multimillion-dollar residences that cater to political elites, business magnates, and international buyers.
Analysts note that these luxury developments reflect a confluence of factors: rising disposable income among Nigeria’s wealthy, a growing expatriate population, and the influx of foreign capital seeking stable returns in real estate. Developers are increasingly targeting high-net-worth clients, often offering amenities such as private gyms, rooftop pools, 24-hour security, and designer interiors.
Economic Drivers Behind the Boom
Several economic trends have fueled the surge in high-end housing:
- Wealth Accumulation and Urbanization
Nigeria is home to Africa’s largest economy and boasts an expanding class of affluent individuals, including entrepreneurs, executives, and professionals in finance, oil, and technology sectors. These buyers are driving demand for properties that meet international standards of luxury. - Foreign Investment
Global investors, attracted by Nigeria’s strategic position and high potential returns, are increasingly participating in the real estate market. Many investors view luxury properties as safe havens for capital amidst currency fluctuations and macroeconomic instability. - Urban Redevelopment Initiatives
Government efforts to modernize urban centers, alongside private-sector investment in infrastructure, have made high-end developments more feasible and attractive. Roads, bridges, and electricity improvements in areas like Victoria Island and Lekki have facilitated the growth of luxury real estate.
Shaping the Skyline
The architectural impact of million-dollar homes is visible across major Nigerian cities. Glass-and-steel high-rises, private estates, and gated communities are redefining skylines that once featured low-rise residential neighborhoods. Developers increasingly use innovative designs, integrating green spaces, smart home technology, and eco-friendly features to appeal to international tastes.
These developments not only symbolize wealth but also signal Nigeria’s growing urban sophistication. The juxtaposition of opulent buildings alongside older, less developed neighborhoods is stark, reflecting the widening wealth gap in urban centers.
Red Flags and Socioeconomic Concerns
While the luxury real estate boom reflects economic dynamism, it also raises a series of concerns:
- Urban Inequality
The proliferation of high-end homes highlights stark socioeconomic disparities. In Lagos, for example, million-dollar villas exist in close proximity to informal settlements and slums lacking basic infrastructure, magnifying urban inequality. - Housing Affordability
As developers focus on premium properties, the supply of affordable housing lags, pushing lower-income families further from city centers and contributing to urban sprawl. This could exacerbate commuting challenges, traffic congestion, and demand for public services. - Regulatory Oversight
Rapid construction of luxury estates sometimes outpaces government planning and oversight. Concerns about zoning compliance, environmental impact, and sustainable urban development have been raised by urban planners and civil society groups. - Money Laundering and Capital Flight
Experts warn that high-end properties can be used as vehicles for money laundering or offshore investment. The opacity of some transactions and limited regulatory transparency make luxury real estate a potential risk for financial crime scrutiny. - Infrastructure Strain
Concentrated luxury developments can strain existing infrastructure, from water and electricity supply to waste management. In some cases, private developers are forced to create independent systems, further highlighting disparities between high-income and low-income areas.
Government and Policy Response
Policymakers face the challenge of balancing economic growth with equitable urban development. Efforts to regulate the real estate sector include:
- Urban Planning Guidelines: Setting minimum standards for building height, density, and environmental impact.
- Taxation and Reporting: Proposals for property transaction reporting aim to improve transparency and reduce illicit capital flows.
- Affordable Housing Initiatives: Programs to incentivize developers to allocate a portion of projects to middle- and low-income housing.
However, enforcement remains uneven, and the luxury real estate market continues to grow faster than regulatory frameworks can keep pace.
The Future of Nigeria’s Urban Landscape
The million-dollar housing boom is likely to continue shaping Nigeria’s cities for years to come. With demand from domestic elites and international investors remaining strong, luxury developments will proliferate, influencing urban aesthetics, property prices, and the socioeconomic fabric of metropolitan areas.
Yet, experts caution that without deliberate policy interventions, the expansion of high-end real estate risks exacerbating inequality, inflating housing costs, and straining urban infrastructure. Sustainable urban development will require a careful balance between economic opportunity, regulatory oversight, and social equity.
Conclusion
Nigeria’s skyline is transforming rapidly, fueled by the rise of million-dollar homes and luxury real estate projects. These developments reflect the nation’s growing wealth, urbanization, and global investment appeal, while simultaneously highlighting pressing concerns over inequality, affordability, and governance.
As Nigeria embraces this new era of urban luxury, the challenge for policymakers, developers, and communities alike will be to ensure that prosperity in the sky does not come at the expense of the urban fabric below.