China’s Desert AI Boom: How Remote Regions Are Becoming Tech Powerhouses
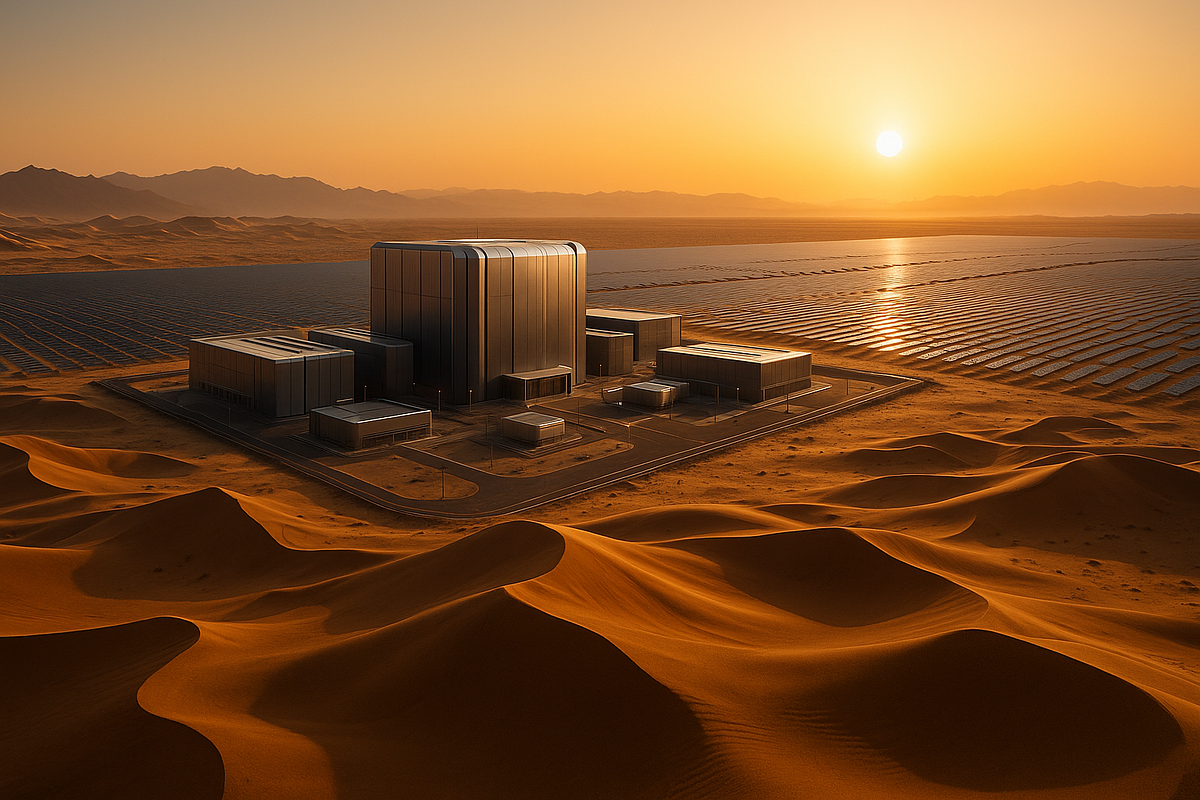

China’s technology landscape is evolving in unexpected ways. Far from the bustling urban centers of Beijing, Shanghai, or Shenzhen, a series of desert regions in northwest China are emerging as hubs for artificial intelligence development. These remote sites—spanning the Gobi and Taklamakan deserts—are attracting massive investments in data centers, AI research, and high-performance computing infrastructure, creating what some analysts call China’s desert AI boom.
Why the Desert?
At first glance, deserts may seem like an unlikely place for cutting-edge technology. But these regions offer several strategic advantages for AI companies:
- Abundant Land: Large tracts of inexpensive land allow for sprawling data centers that would be prohibitively costly in crowded cities.
- Cool, Dry Climate: Desert conditions reduce the energy required for cooling server farms, improving operational efficiency.
- Energy Access: Proximity to renewable energy projects, particularly solar and wind farms, supports the massive power demands of AI training.
China’s government has actively promoted these areas as technology zones, offering tax incentives and subsidies to attract domestic and international AI firms.
A Surge of Investment
In recent years, Chinese tech giants and startups alike have poured billions into desert AI hubs. Companies specializing in generative AI, cloud computing, and autonomous systems are establishing research facilities and supercomputing centers.
State-owned enterprises are also involved, building infrastructure to support both commercial and military applications. Analysts note that this wave of investment is part of China’s broader strategy to become a global leader in AI by 2030, reducing reliance on foreign technology and cultivating homegrown talent.
The Role of Supercomputing
AI development requires extraordinary computing power. Desert AI hubs are home to some of China’s largest supercomputers, which handle tasks from natural language processing to climate modeling. These facilities operate 24/7, processing massive datasets that fuel machine learning algorithms and support breakthroughs in areas like autonomous driving, robotics, and precision medicine.
The combination of abundant energy, low land costs, and government support allows China to scale its computing capacity faster than most other countries.
Economic and Social Impacts
The AI boom is transforming remote desert regions into economic centers. Local communities are seeing new jobs in construction, operations, and high-tech research, while ancillary services—from logistics to housing—are also expanding.
However, challenges remain. Desert infrastructure is vulnerable to sandstorms, water scarcity, and environmental degradation. Balancing rapid technological growth with sustainable development is a pressing concern for both companies and local authorities.
Strategic Implications
China’s desert AI hubs are more than an economic experiment—they have geopolitical significance. By concentrating AI research and computing resources in remote regions, China can pursue advanced AI capabilities in relative security, away from prying eyes and potential cyber threats.
Experts warn that these hubs could accelerate China’s leadership in AI-driven industries, from defense and cybersecurity to autonomous vehicles and healthcare technology. The concentration of talent, computing power, and data access in desert regions represents a strategic advantage in the global AI race.
Looking Ahead
As AI technologies continue to evolve, China’s desert hubs may serve as both testing grounds and production centers for next-generation applications. International observers are closely monitoring these developments, recognizing that the outcomes could reshape the global technological balance.
While urban tech centers will remain critical for innovation and entrepreneurship, the desert AI hubs demonstrate China’s willingness to exploit unconventional geography for strategic technological gains. They are a vivid example of how geography, policy, and ambition can converge to create unexpected centers of innovation.
Conclusion
The rise of AI hubs in China’s deserts illustrates a new phase in the global technology race—one in which innovation is no longer confined to cities or traditional industrial clusters. By harnessing remote regions for high-tech development, China is building an AI ecosystem that combines scale, power, and strategic depth.
The world is watching as these barren landscapes are transformed into oases of artificial intelligence, offering insights into how nations may approach the future of technology, security, and economic development.